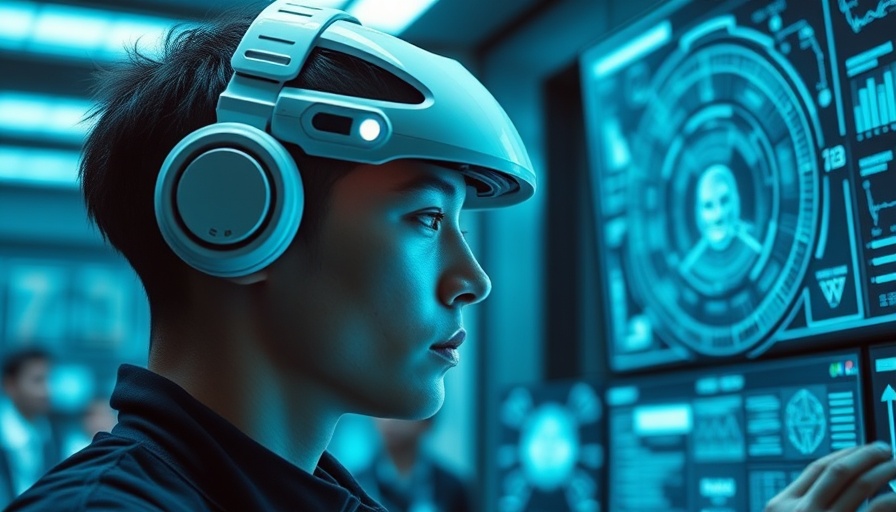

A Leap Forward: Man Controls Robotic Arm With Thoughts
In an extraordinary breakthrough for neuroscience and technology, researchers at the University of California, San Francisco, have developed a brain-computer interface (BCI) that enables a paralyzed man to control a robotic arm using only his thoughts. This revolutionary advancement marks a significant step toward enhancing the quality of life for individuals with paralysis.
Understanding Brain-Computer Interfaces
The premise of a BCI is fascinating: it relays brain signals to a computer, allowing users to execute actions by simply imagining them. In this case, the participant, who had become paralyzed due to a stroke, was equipped with sensors implanted on the surface of his brain. These sensors picked up signals associated with movement, even though the participant was physically incapable of carrying out those movements.
The Research Breakthrough
What sets this research apart is its duration; previous BCIs typically struggled to maintain functionality beyond a couple of days. However, this device operated effectively for an impressive seven months. This longevity can be attributed to an AI model that learns from the gradual changes in brain activity as the participant repeatedly imagined specific movements.
Implications For The Future
The results of this research touch not just the domain of bioengineering but extend into the fields of AI and rehabilitation. Neurologist Karunesh Ganguly, a key investigator in the study, highlighted the potential of melding human cognitive processes with AI frameworks as a means to produce more lifelike functions in robotic systems. This fusion could lead to the creation of sophisticated assistive devices that could one day replicate human dexterity and control.
Psychological Impact of Technological Innovation
This advancement also speaks volumes about the psychological ramifications for those affected by paralysis. The ability to perform actions mentally can positively influence self-esteem and reduce feelings of helplessness. It empowers users with a sense of agency—an essential component of mental health and well-being.
Looking Ahead
With ongoing research and development, this technology may one day become a staple in assistive devices for individuals with disabilities. As the BCI gains sophistication through iterative learning from the user's brain patterns, the applications in various fields—ranging from robotics to neuroprosthetics—appear boundless.
In conclusion, as we navigate these exciting advancements in AI and technology, understanding their potential impact becomes vital. It is not just about creating machines that mimic human actions but about crafting solutions that could bring genuine change to people's lives.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment