Understanding the CYCLEATTRS Option in PROC SGPLOT
The CYCLEATTRS option in the SAS PROC SGPLOT procedure provides a nuanced approach to managing how visual representations of data can be manipulated and displayed. For many data enthusiasts, especially those venturing into data visualization, understanding the default behavior of attributes assigned to overlaid plots is crucial for effective communication of data insights.
Why Attributes Matter in Data Visualization
Attributes such as color, size, line style, and marker symbol play a fundamental role in data visualization as they enhance readability and comprehension for viewers. When presenting complex datasets, a clear distinction between multiple series can turn confusion into clarity. For instance, data visualizations that feature diverse datasets can benefit tremendously from the automatic cycling of attributes, allowing each series to be quickly distinguishable.
The Default Behavior and Its Impact
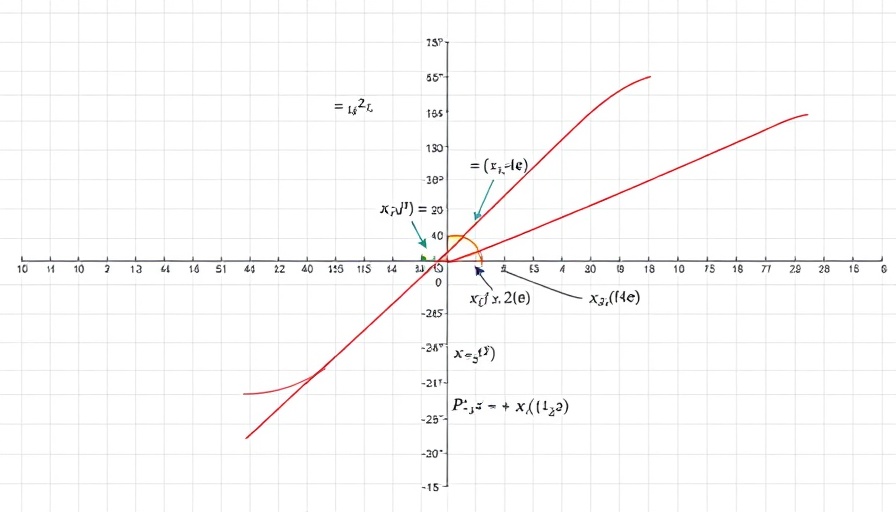
When working with PROC SGPLOT, users may find surprise in how default settings for attributes function based on plot types. According to Rick Wicklin, who discusses the mechanics of this procedure, when multiple series statements are all of the same type (e.g., all SERIES), the default setting for attributes is CYCLEATTRS. This means that color and other visual attributes will automatically differ amongst the series, thus enhancing distinguishability.
Conversely, when mixing plot types (for example, a SERIES vs. SCATTER), attributes default to being the same, which can lead to visual confusion. Therefore, understanding how CYCLEATTRS might impact your visualizations can greatly affect the message conveyed through the data.
Utilizing CYCLEATTRS Effectively
The ability to override default behaviors using CYCLEATTRS provides flexibility for data scientists and analysts. When visual components interact in a way that may confuse viewers, using the NOCYCLEATTRS option can provide uniformity that aids understanding, especially when various types of data points are being compared.
To demonstrate the different behaviors, consider the example of plotting the exponential function alongside its Taylor series approximates. By ensuring your data visualization adheres to these principles, you can strategically highlight differences or similarities with the appropriate use of color and line styles.
Practical Insights to Implement
To maximize the effectiveness of CYCLEATTRS, here are several practical tips:
- Know Your Data: Always evaluate the type of data you are working with. Adjust the attributes accordingly to suit the visualization requirements.
- Experiment with Examples: Engage with the PROC SGPLOT using varying datasets and observe how the attributes change with different settings of CYCLEATTRS.
- Seek Feedback: Show your visualizations to peers who may not be data-savvy and observe if they can easily interpret the data; adjust attributes for clarity where necessary.
Where to Go from Here
Understanding the intricacies of data visualization options like CYCLEATTRS not only enhances personal proficiency but also significantly impacts how data-driven insights are shared and understood in a team or organizational context. In today's technological landscape, refined data storytelling has become a pivotal component of successful AI learning paths and data science principles.
As industries continue to embrace AI science in their operations, being equipped with visualization skills can open doors to effective communication and innovative problem-solving. Embrace these insights as foundational aids in your ongoing journey of learning and harnessing the power of data.
Stay inspired, stay curious, and continue your exploration in the tech landscape, as understanding complex tools gives you a competitive edge. The journey in AI learning is ever-evolving, making it essential to adapt and apply these tools effectively.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment